Collagen has been described as the most abundant protein in the body, forming around 30 percent of the human body’s protein content. It is crucial for various functions within the body, such as wound healing, providing structural support, and offering a framework for body tissues. Collagen is also known to have an essential role in the skin’s aesthetics, being responsible for its firmness, resilience, and youthful appearance. Today, we will discuss the role of collagen in the body in detail.
What is collagen?
Collagen is a protein composite composed of three amino acids: proline, hydroxyproline, and glycine, arranged in a triple helix chain structure. This structure makes it unique and strong, giving it the ability to provide support to the body’s tissues.
Different Types of Collagen
There are 28 types of collagen, but the most common four types are listed below.
Type 1 Collagen: Type 1 is the most abundant collagen in the body and is present in various connective tissues such as the skin, bones, tendons, ligaments, and teeth. It has a critical role in providing structure, support, and strength to these tissues.
Type 2 Collagen: Type 2 is found in cartilage and has a significant role in the joint’s overall health and mobility.
Type 3 Collagen: Type 3 is found in the skin, arteries, and intestines, playing a vital role in the skin’s firmness and the elasticity of the larger blood vessels.
Type 4 Collagen: Type 4 is found mainly in the basement membrane and plays a vital role in the proper functioning of the tissues and organs.
Functions of Collagen in the body
Collagen plays many roles in the body, each of which contributes to the overall well-being of the body. Some of the essential functions of collagen in the body are:
Structural Support: Collagen is the most abundant protein that makes up various connective tissues, such as bones, cartilage, and tendons. It provides structure and strength, making the bones and joints less susceptible to injury and fractures.
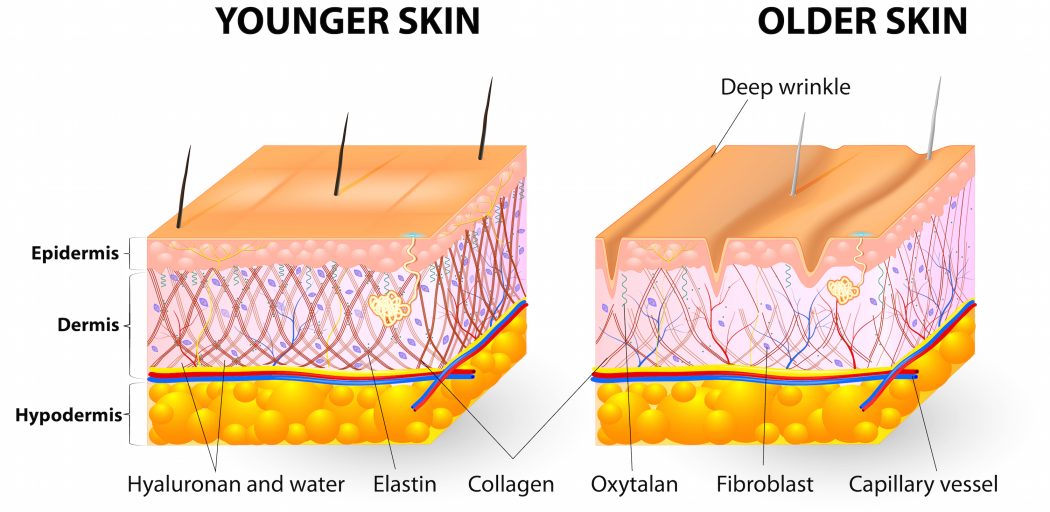
Skin Health: Collagen is responsible for the skin’s firmness, elasticity, and hydration, which are essential for maintaining a youthful appearance. As collagen deteriorates with age, wrinkles and fine lines start to appear.
Wound Healing: Collagen is necessary for healthy wound healing. It forms a vital part of the extracellular matrix, which supports cell migration and tissue growth.
Digestive Health: Collagen is a critical component of the intestinal wall that lines the digestive tract. It is involved in regulating the passage of nutrients and waste products.
Cardiovascular Health: Collagen plays a significant role in maintaining the structural integrity of the blood vessels, keeping them in good health, and preventing the risk of stroke or heart attack.
Hair and Nail Growth: Collagen is essential in maintaining healthy hair and nails. It provides the necessary structure for cells to grow, strengthening the hair and nails.
Bone Health: Collagen plays a vital role in maintaining bone health. It forms an essential part of the bone matrix, providing support and strength to the bones.
The Effects of Collagen Deficiency
Collagen deficiency can lead to various health problems, such as:
Skin Aging: Loss of collagen in the skin results in wrinkles, fine lines, and the loss of elasticity contributing to an aged appearance.
Joint Pain: Collagen loss leads to the breakdown of cartilage that causes joint pain, stiffness, and inflammation.
Digestive Issues: Collagen loss can lead to digestive problems, such as leaky gut syndrome, abdominal pain, and bloating.
Bone Fractures: Collagen deficiency can lead to weak and brittle bones, resulting in fractures and the increased risk of osteoporosis.
Muscle Loss: Collagen loss can lead to muscle weakness, loss of strength, and the decreased ability to exercise and perform daily activities.
How to Increase Collagen Production
As we age, the natural production of collagen declines. To maintain collagen levels, individuals can adapt some healthy habits:
Sun Protection: Sun’s harmful UV rays can damage the skin, leading to the breakdown of collagen fibers. Sun protection and avoiding prolonged sun exposure can help.
Strengthen gut health: Maintaining gut health by eating a nutrient-rich diet and avoiding food with allergens can reduce the chance of inflammation that may lead to a loss of collagen.
Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help increase collagen production in the body, which helps maintain the skin’s elasticity and overall body strength.
Adequate sleep: Proper rest and a good night’s sleep promote healthy collagen production.
Nutritional supplements: Collagen supplements or food items rich in amino acids like glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline can promote collagen production.
Conclusion: Collagen is a vital protein that performs various essential functions in the body. Maintaining healthy collagen levels can help maintain healthy skin, bones, and joints, and promote overall wellbeing. Lifestyle changes, a nutrient-rich diet, and reducing sun exposure are some of the practical ways to maintain healthy collagen levels.